Codeine
Codeine, an opioid analgesic, was originally approved in the US in 1950 and is a drug used to decrease pain by increasing the threshold for pain. Codeine may cause serious or life-threatening breathing problems, especially during the first 24 to 72 hours of your treatment . It is a medication used in the management and treatment of chronic pain. It is in the opioid class of medications. This is an oral prescription opioid (narcotic) drug most commonly used to treat mild-to-moderate pain, as a cough suppressant . Codeine is an opioid pain-relief medicine used for the short-term relief of mild to moderate pain. · It is not usually recommended for the treatment of chronic .Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine. .
Buy Codeine
-
- codeine
Actavis Promethazine Codeine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.61 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.46 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.66 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine for sale
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.64 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine paracetamol
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.82 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine phosphate 30mg
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.59 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine sirop
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.56 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine sulfate
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.67 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist
-
- codeine
codeine for sale
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.64 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Buy codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.48 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
dafalgan codeine 500 mg
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.54 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
klipal 600
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.51 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
best cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.47 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
cough syrup uses
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.51 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.55 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cough syrup brands
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.49 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cough syrup australia
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.75 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
dafalgan codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.82 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
paracetamol codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.35 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codéine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.11 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
klipal codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.75 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codéine médicament
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.32 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
paracetamol codeine effets secondaires
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.54 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine for sleep
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.75 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine brand name
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.62 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine class
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.45 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
cough syrup for covid
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.83 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
cough syrup for kids
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.54 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
cough syrup names
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.41 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
cough syrup adults
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.61 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
top 10 cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.50 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
cough syrup for dry cough
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.32 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine hydrochloride
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.38 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine tablets
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.29 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine side effects
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.37 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.69 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
promethazine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.49 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis pill
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.66 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis xanax
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.45 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis elizabeth llc
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.46 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis tretinoin cream 0.025
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.34 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis lidocaine patch 5
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.81 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis codeine kopen
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.59 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.63 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
buy Actavis
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.58 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine effet
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.52 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
buy actavis cough syrup online
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.69 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Promethazine Codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.58 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cena
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.47 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
actavis cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.53 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine in pregnancy
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.46 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine phosphate 30mg دواء
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.61 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine linctus
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.63 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine phosphate
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.46 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.23 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine comprimé
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.67 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Co-codamol
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.50 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Vopac
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.50 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Tylenol with Codeine No 3
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.60 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Tylenol wCodeine 4
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.59 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Tylenol wCodeine 3
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.60 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Tylenol wCodeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.47 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Sizzurp
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.54 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Pyregesic-C
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.60 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Capital wCodeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.58 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
APAP wCodeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.33 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Purple Drank
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.51 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Lean
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.81 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Captain Cody
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.45 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Little C
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.48 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Schoolboy
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.60 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine phosphate 30mg
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.59 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.66 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine paracetamol
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.82 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine sulfate
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.67 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine sirop
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.56 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
Actavis Promethazine Codeine cough syrup
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 2.61 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist -
- codeine
codeine
- $200.00 – $600.00
- Rated 3.46 out of 5
- Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Add to WishlistAdd to Wishlist
codeine cough syrup
Drug interactions
Dosage information
During pregnancy or Breastfeeding
Reviews (57)
Drug images
Compare alternatives
Pricing & coupons
En español
Drug class: antitussives
Patient resources
Drug Information
Codeine (Advanced Reading)
Codeine Tablets
Codeine Oral Solution
Professional resources
Prescribing Information
Related treatment guides
Cough
Pain
Diarrhea
codeine phosphate
Codeine. Revised 03/2021. West-Ward Pharmaceuticals Corp.
Further information
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use codeine only for the indication prescribed. Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine.
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances. May not be suitable for some people including children of any age who have undergone a tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy, people with pre-existing respiratory depression or respiratory disease, with seizure disorders or a head injury, people with gastrointestinal obstruction, or recent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
Should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding unless specifically recommended and monitored by a doctor. Can cause life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in a newborn. Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine.
codeine phosphate 30mg دواء
Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine. Codeine is addictive (habit-forming) and potentially abusable. should only be used short-term at the lowest effective dose and only when other nonopioid analgesics are not effective. Tolerance can also develop to codeine’s analgesic effect (this means that the same dose does not provide as much pain relief as before). Legitimate supplies of products containing codeine may be sought out by drug seekers.
Abrupt discontinuation of the bottle in a person who has become physically dependent on it may lead to a withdrawal syndrome and symptoms such as restlessness, pupil dilation, watery eyes and a runny nose, sweating, muscle aches, insomnia, irritability and gastrointestinal complaints.
Rarely, serious, life-threatening, breathing problems may occur attributable to the component. The risk is greater with higher dosages of it, in people with pre-existing respiratory disease, in seniors or the frail, or in those taking other medications that cause respiratory depression (such as benzodiazepines). Not for use in children under the age of 18.
Codeine may interact with several drugs, including those that affect hepatic enzymes CYP 3A4 or CYP 2D6, and those that also cause respiratory depression (such as other opioids, benzodiazepines, and alcohol).
Interaction or overdosage may also cause serotonin syndrome. Symptoms include mental status changes such as agitation, hallucinations, coma, or delirium; a fast heart rate; dizziness; flushing; muscle tremor or rigidity; and stomach symptoms (including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea). Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine.
Long-term use of cough medicine also affects the endocrine system, which may cause symptoms such as sexual dysfunction, an absence of periods, or infertility. Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine.
codeine 30mg
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea.It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain.
Drowsiness or dizziness which may impair reaction skills and affect a person’s ability to drive or operate machinery. Avoid alcohol.
also slows down the motility of the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal pain. Laxatives may be required. Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain or cough. Learn what to expect from withdrawal if you become dependent on or addicted to codeine.
may also affect blood pressure, manifesting as dizziness when standing; and stimulate histamine release, which may cause symptoms such as flushing, itchiness, sweating, or red eyes.
Babies born to mothers who are physically dependent on it will also be physically dependent.
Marked differences may exist in the analgesic effect provided by due to genetic variations in the CYP 2D6 liver enzyme responsible for metabolizing into morphine. Consider alternative analgesics if codeine is not having the desired pain-relieving effect.
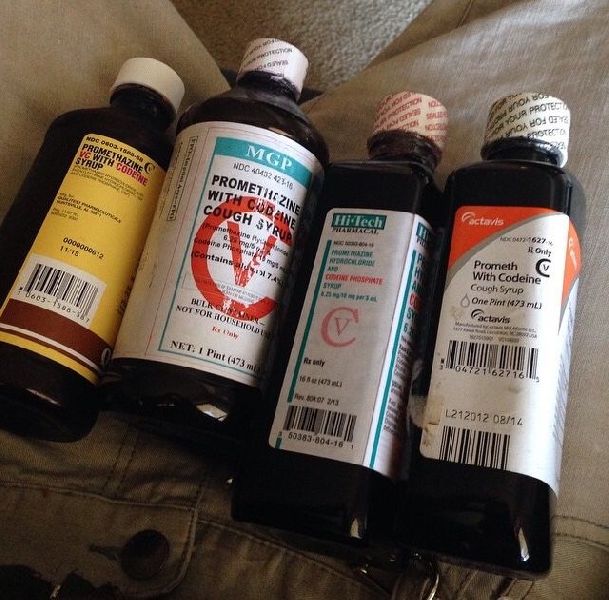





codeine linctus
Note that this list is not all-inclusive and includes only common medications that may interact with codeine. You should refer to the prescribing information for codeine for a complete list of interactions.
codeine comprimé
Do not double up on other medications containing codeine (several cold and flu remedies also contain this ).
Avoid alcohol while taking . Alcohol can contribute to the sedative effects of and also increase the risk of respiratory depression.
may make you feel dizzy when getting up from a lying down or sitting position to standing. Always get up slowly, but talk with your doctor if this dizziness results in a fall.
Codeine may cause constipation which can be relieved with laxatives. Drink 6 to 8 full glasses of water daily to prevent this effect. Talk to your doctor if you experience any troublesome side effects of before using a laxative..
Seek urgent medical advice if you experience any excessive sedation, breathing difficulties, wheezing, rash, itching, or facial swelling. Call emergency services if you suspect somebody has overdosed on (pinpoint pupils may be indicative of overdosage).
Do not use during pregnancy or breastfeeding unless specifically recommended by your doctor.
Keep this medicine in a safe place and out of the reach of children and pets. Accidental ingestion can result in a fatal overdose of codeine, especially in children. Never give it to children under the age of 18.
1. How it works
Codeine is an opioid analgesic (pain-reliever) that is related to morphine.
Codeine works by weakly binding to a specific opioid receptor, known as the mu-opioid receptor, but with much less affinity than morphine, which means its analgesic (pain-relieving effects) are much less.
Codeine belongs to the group of drugs known as opioids or opioid analgesics. Codeine may also be called a narcotic analgesic.
2. Upsides
May be used to treat mild-to-moderate pain that is unrelieved by nonopioid analgesics.
Generic codeine is available.
3. Downsides
If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medication or have no other medical conditions, side effects you are more likely to experience include:
how long does lean stay in your system
Note: In general, seniors or children, people with certain medical conditions (such as liver or kidney problems, heart disease, diabetes, seizures) or people who take other medications are more at risk of developing a wider range of side effects. View complete list of side effects
4. Bottom Line
Codeine is an effective pain-reliever; however, it is addictive, may cause constipation, and its pain-relieving effects vary markedly between individuals. should only be used for pain relief when other simpler analgesics, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, are not appropriate.
5. Tips
May be taken with or without food. Do not take more codeine than you have been prescribed. Codeine should be used short-term only. Long-term use may lead to addiction and dependence. may need to be discontinued slowly depending on the duration of use. Talk to your doctor about a tapering schedule. Never share your codeine with anyone. Do not keep your leftover medicine. Ask your pharmacy when the next take-back program is.
May cause sedation and affect your ability to drive or operate machinery. Do not drive or perform other hazardous tasks if codeine affects you in this way.
Use short-term (three days or less) only. Not recommended for long-term use.
Tell your doctor if you think you have become addicted to it or the usual dosage does not appear to be working.
6. Response and effectiveness
The analgesic effect of reaches a peak in about two hours and the effects last for between four to six hours.
About 70-80% of a dose of codeine is metabolized by the liver into a number of metabolites, some active and some inactive. One of these active metabolites is morphine. About 5-10% of codeine is metabolized into morphine by the hepatic enzyme, CYP2D6. Experts believe some of the analgesic properties of it are due to it being converted into morphine. Note that up to 10% of Caucasians, 6% of Mexican-Americans, and 5% of African-Americans are poor metabolizers at CYP2D6 and are unlikely to metabolize codeine into morphine. 30% of Ethiopians, 20% of Saudis, 10% of Portuguese and Greeks, and 4% of North Americans are ultra-rapid metabolizers at CYP 2D6 and may experience excessive side effects, such as extreme sleepiness, confusion, and shallow breathing, even with normal dosages of it
7. Interactions
Medicines that interact with may either decrease its effect, affect how long it works for, increase side effects, or have less of an effect when taken with it . An interaction between two medications does not always mean that you must stop taking one of the medications; however, sometimes it does. Speak to your doctor about how drug interactions should be managed.
Common medications that may interact with codeine include:
antibiotics, such as erythromycin
antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants (eg, amitriptyline), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (eg, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, and tranylcypromine), or SSRIs (eg, fluoxetine, sertraline)
antifungal agents, such as itraconazole and ketoconazole
anticonvulsants, such as carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, or primidone
antimigraine agents such as sumatriptan
antipsychotics (such as butyrophenones, phenothiazines, or thioxanthenes) and atypical antipsychotics (eg, olanzapine, quetiapine, ziprasidone)
any medication that may cause drowsiness, such as amphetamines, azelastine, benzodiazepines (eg, diazepam, lorazepam), first-generation antihistamines (such as doxylamine or promethazine), metoclopramide, or opioids (such as hydrocodone, morphine)
buprenorphine
HIV medications such as darunavir or ritonavir
muscle relaxants, such as cyclobenzaprine
naltrexone
other medications that are CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers
pentazocine
rifampin.
Avoid drinking alcohol or taking illegal or recreational drugs while taking codeine.
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................…...........................................